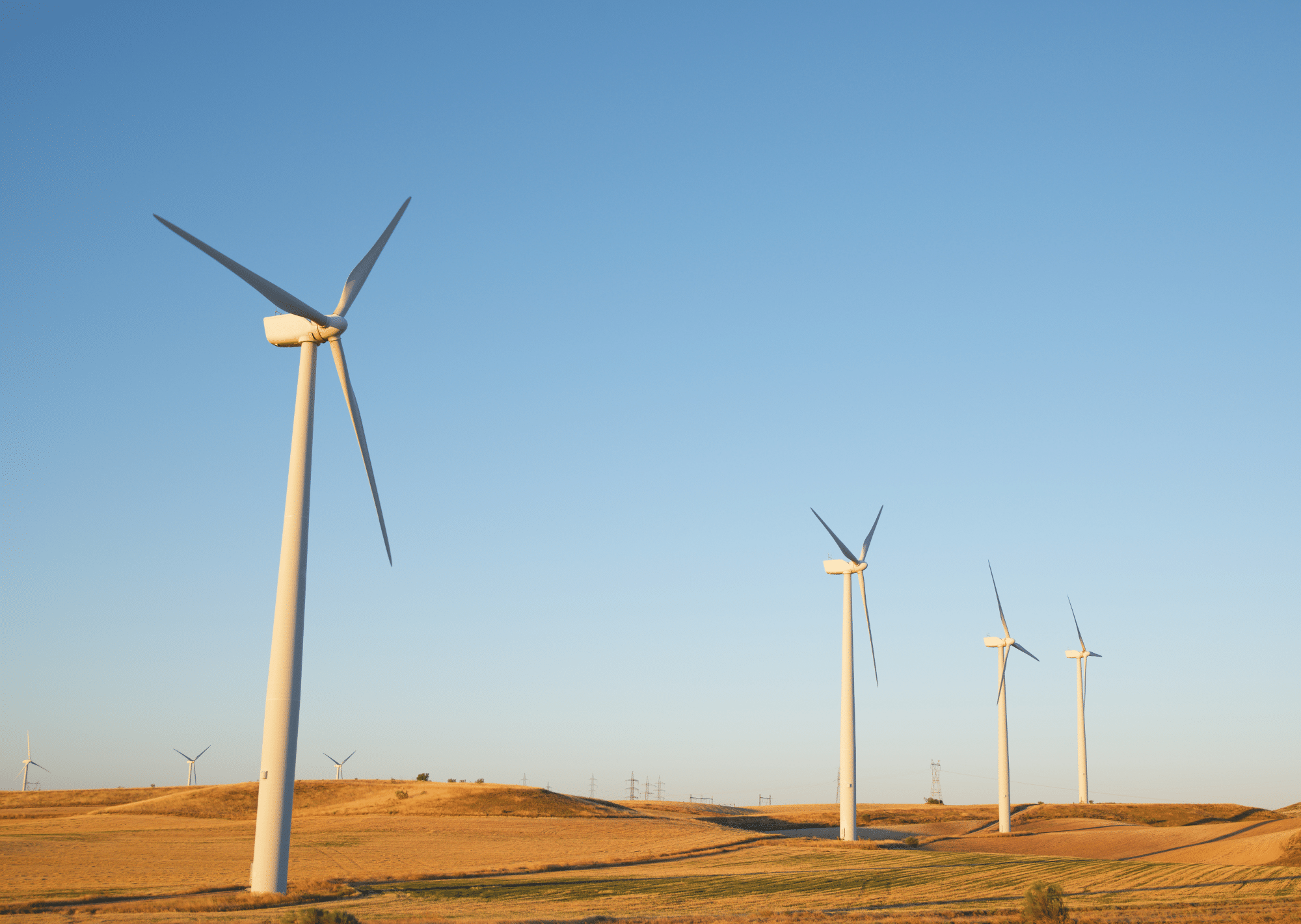
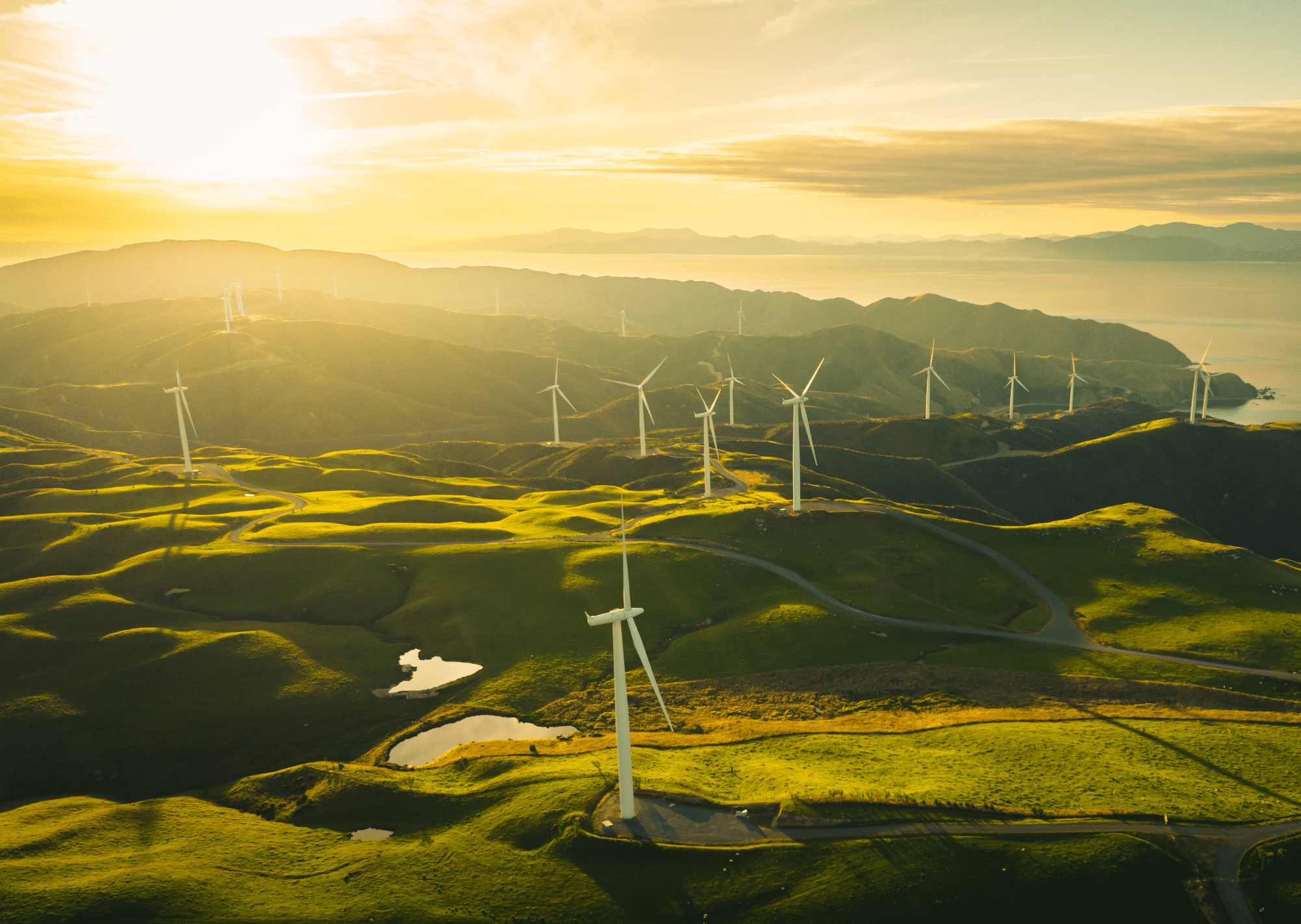
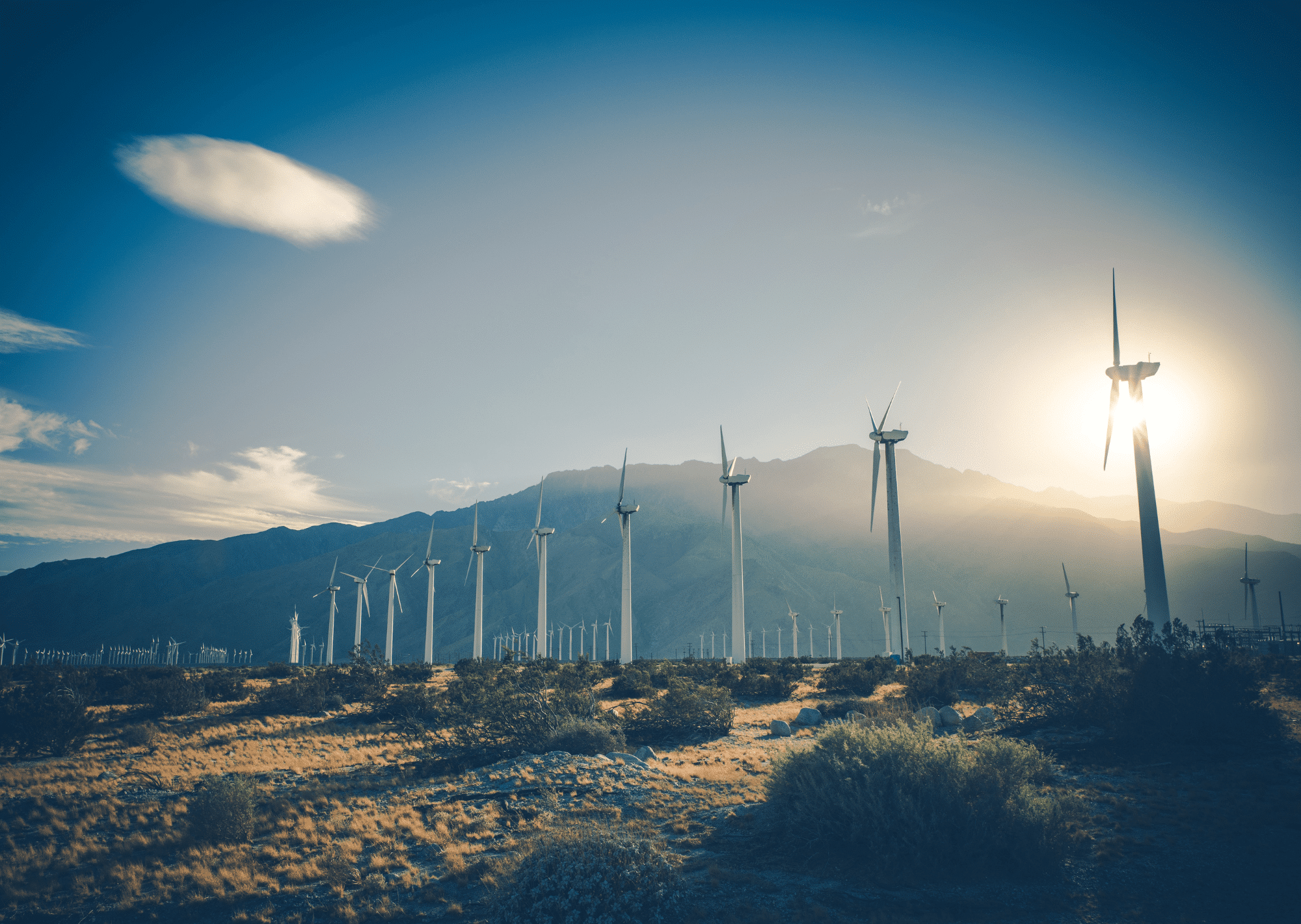
Wind provides an important renewable energy source. For years, old-fashioned windmills were used for wind energy, but times have changed and so has the technology around wind energy. Today, wind turbines are the most common way that wind energy is collected. Wind turbines take the power of wind and turn it into electricity. This electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, and sometimes full cities. Wind turbines and wind farms are popping up all over, because of that, we think it’s important to look into how wind turbines work.
What are wind turbines?
Before we can go too deep into how wind turbines work, it is important to review what wind turbines are.
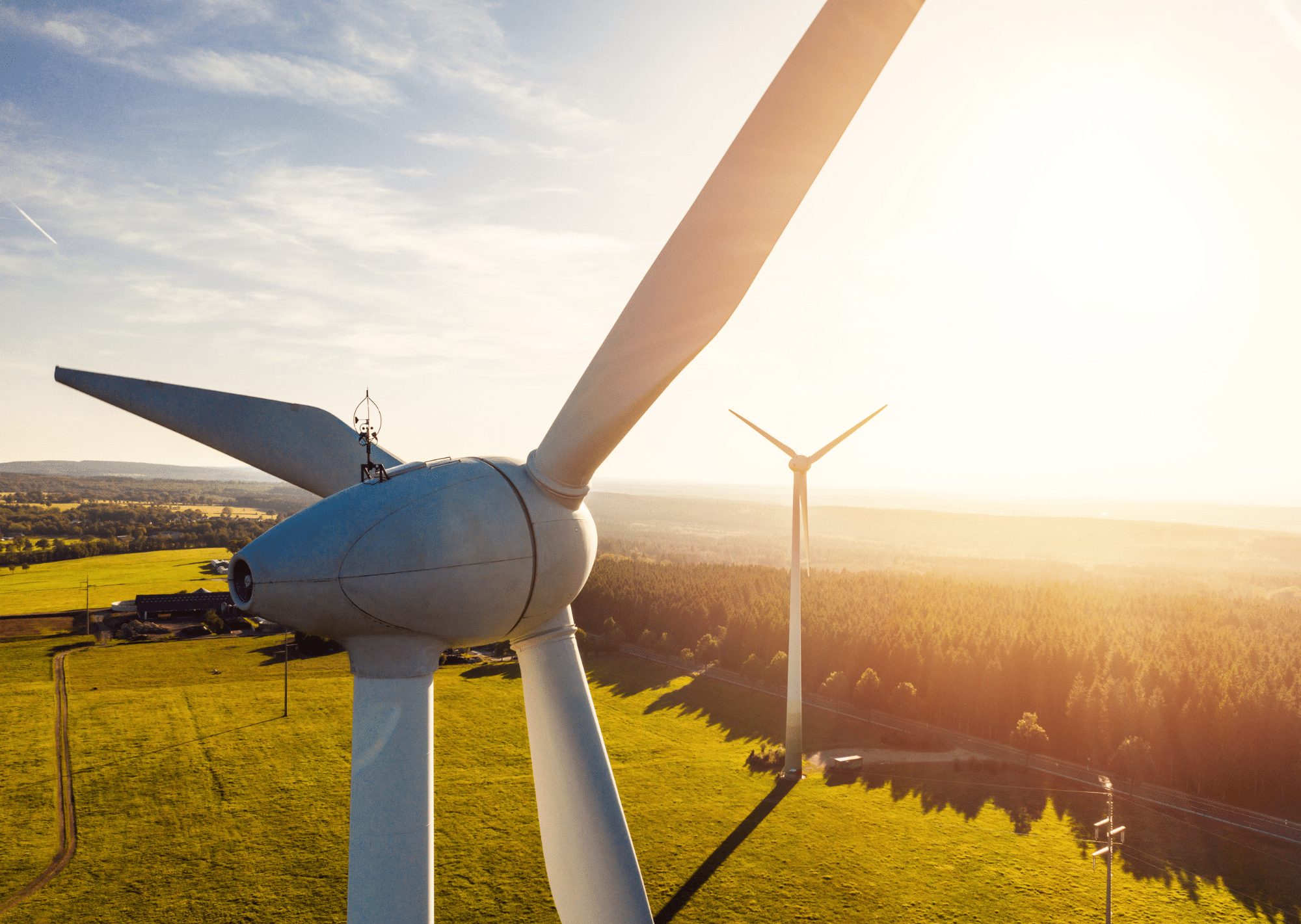
Wind turbines are the modern version of a windmill. They are mounted high on a tower to capture as much energy as possible. They are usually at 100 feet or more above ground, so that they can take advantage of the faster and less turbulent wind. A wind turbine usually has, two or three blades that are mounted on a shaft to form a rotor, these blades capture the wind and spin to create electricity.
What are the parts of a wind turbine?
To really understand how wind turbines work, you need to understand it’s parts. Wind turbines consist of rotor blades, a box beside them called a nacelle, and of course, the tower. Let’s review a little further.
- Rotor Blades: The blades of a wind turbine act much like an airplane wing. One side of the blade is curved and the other is flat. The wind flows more quickly along the curved edge, creating a difference in pressure on either side of the blade. The blades are then “pushed” by the air in order to equalize the pressure difference, causing the blades to turn.
- Nacelle: The nacelle is a cover housing that contains all of the generating components in a wind turbine, including the generator, gearbox, drive train, and brake assembly. The rotor blades are linked to the generator via the gears. The gears speed up the moderately slow rotor blade rotation to a faster pace, the wind is then converted into electricity via the generator.
- Tower: The tower of a wind turbine can not be missed. Much like the blades, it stands out, literally. The blades and nacelle are mounted at the top of the tower. The tower is built to hold the rotor blades off the ground and at an ideal wind speed location and height. The height of the tower varies by location. The general rule is to install a wind turbine on a tower with the bottom of the rotor blades at least 30 feet above any obstacle that is within 300 feet of the tower.
What are some other interesting facts about how wind turbines work?
While the parts helped to provide a little insight into how wind turbines work, you may still have some unanswered questions. We are going to review some common questions about wind turbines below.
- What is a wind farm? Odds are that at some point, you have seen a lot of wind turbines all in the same area. This is called a wind farm. A wind farm is a group of wind turbines, usually built in areas known to be windy on a regular basis. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an extensive area. Wind farms can be either onshore or offshore.
- Why are wind turbines usually light in color (white or light grey)? The light color of wind turbines is to make them more aesthetically pleasing. The lighter colors allow them to blend in better with their background, especially when it is cloudy.
- How windy does it need to be for wind turbines to work? Wind turbines can operate in anything from very light to very strong wind speeds. They generate around 80% of the time, but not always at full capacity.
- Why do wind turbines sometimes appear to be off? The main reason is that there is not enough wind to power the blades, or there is too much wind that could damage the turbine. Another reason is for routine maintenance and repairs. Also, if the turbines are producing more electricity than what is needed, the grid may not be able to handle it, so they stopped until needed again.
- When was the wind turbine first created/used? The first known wind turbine that was used to produce electricity was in 1887. It was created by Professor James Blyth to power his holiday home in Scotland.
- When and where was the first wind farm? The first wind farm was in the United States in 1980. It consisted of 20 wind turbines and was installed on the shoulder of Crotched Mountain in New Hampshire.
How wind turbines work, and wind energy in general, is fascinating to us at Mackinnon & Partners. We were founded on a wealth of energy sector experience and, we have a vision of becoming the premier provider of global recruitment solutions to the Renewable Energy & Technology sector.
Wind is one of our key markets where we aim to provide first class candidates. Our senior management has over 40 years of experience in the industry, globally and within the U.S.
Our consultants are sector specialists and passionate advocates for the Renewables Economy. Our team of experts allows us to provide our clients and candidates with exceptional support. Contact us today to learn more about how we can connect you to your next career or help you find the ideal candidates.
- Construction Jobs Recruitment Agency - April 15, 2024
- What is Recruitment Process Outsourcing? - April 8, 2024
- The Benefits of Outsourcing Recruitment to a Specialist Agency - March 27, 2024